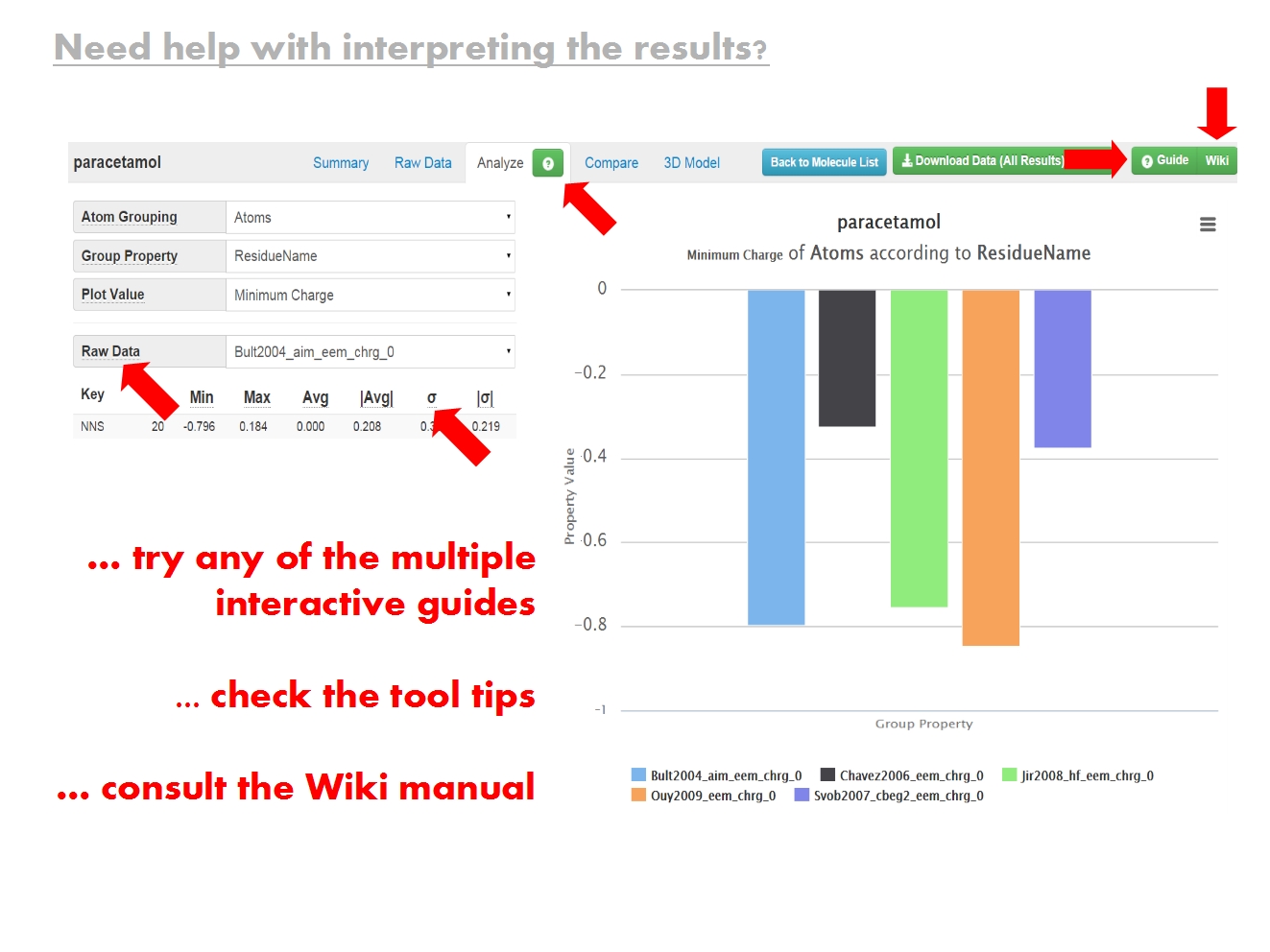
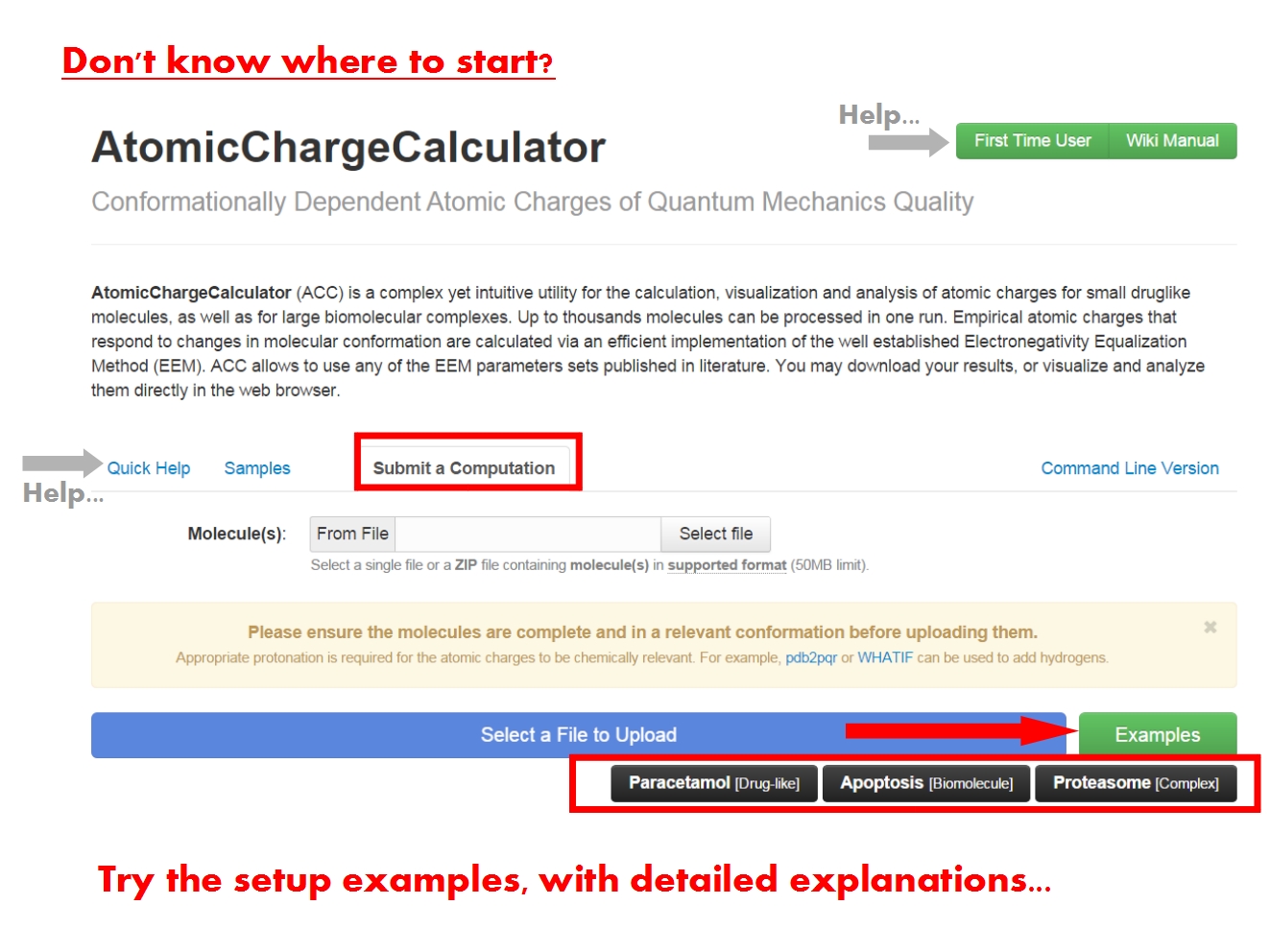
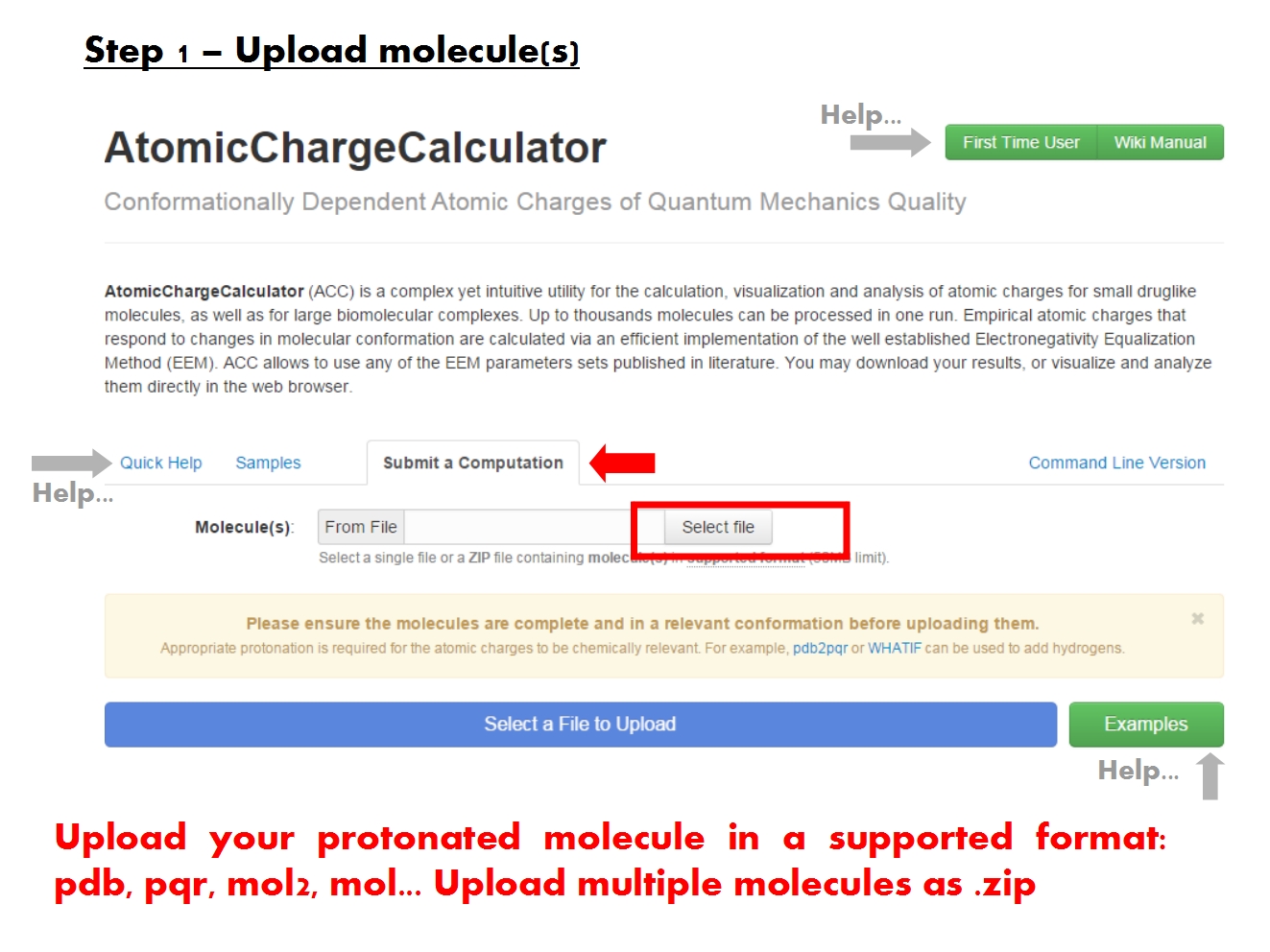
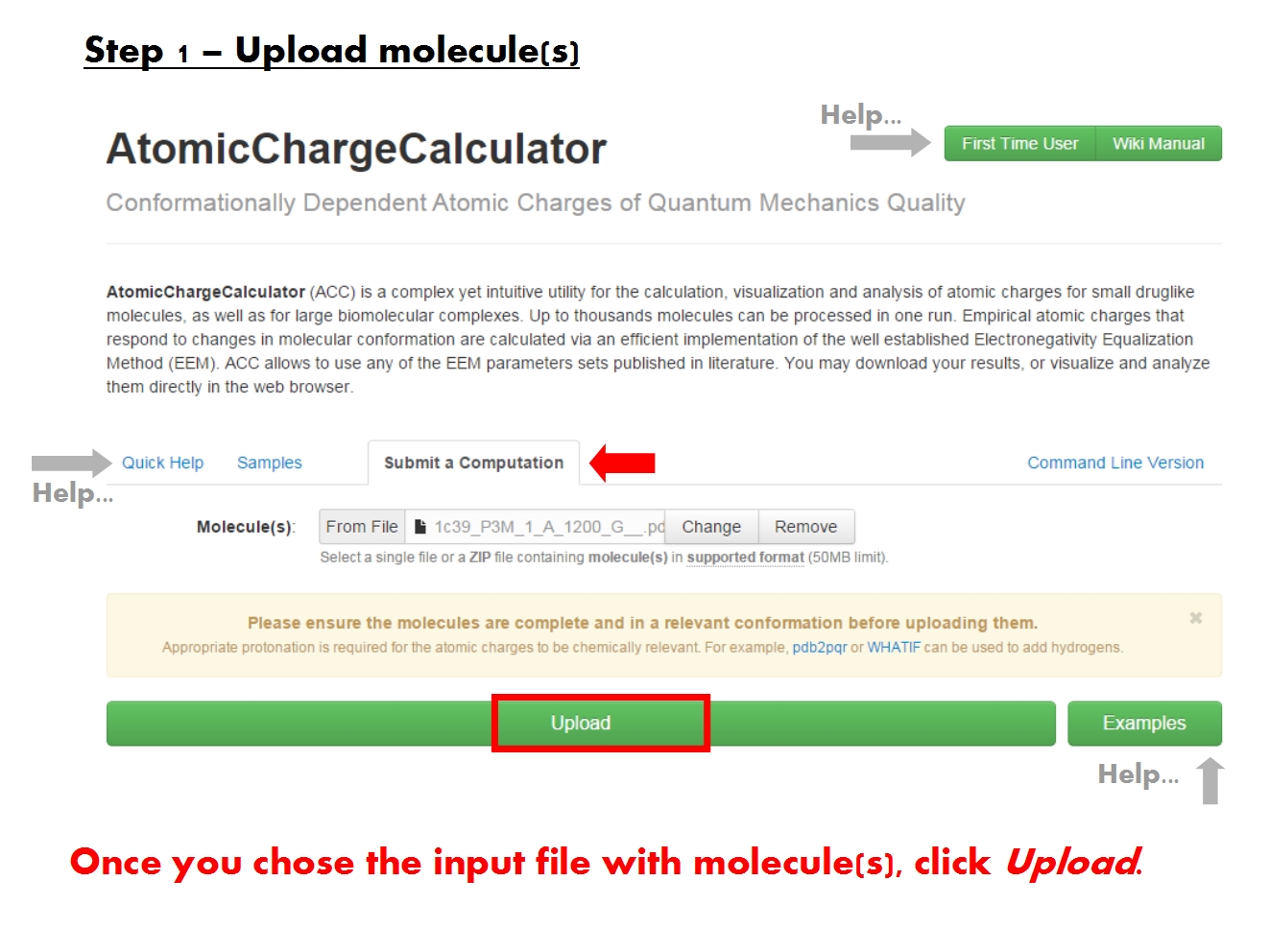
ChargeCalculator:Job submission
The ACC submission page contains a brief description of ACC, and is further organized into several tabs. Since this is your first contact with ACC, the support tabs Quick Help and Samples help you get started, with basic information and examples of ACC use cases.
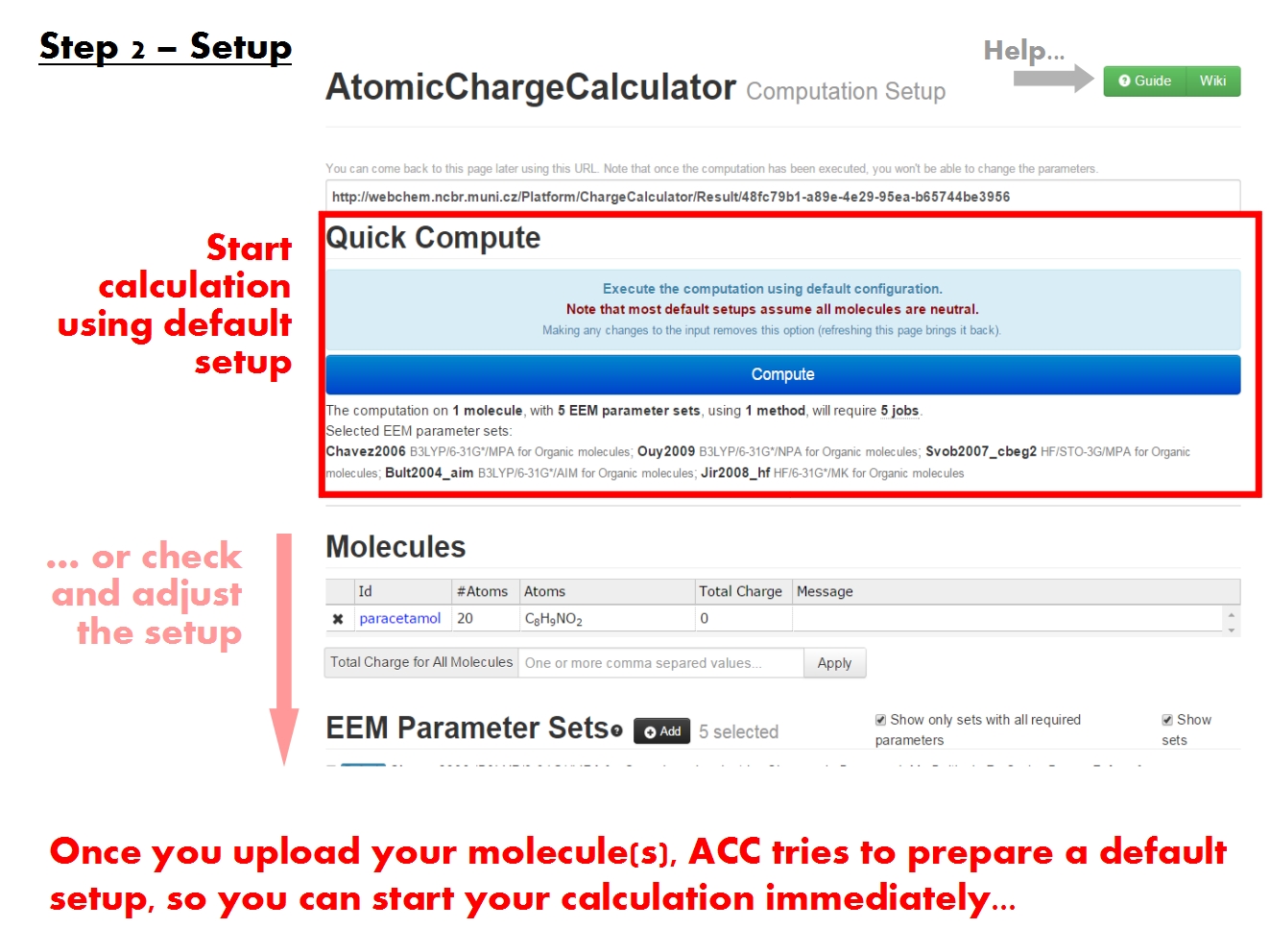
You may submit an atomic charge calculation in 3 easy steps, namely: upload your molecule(s), setup the computation, and finally start the calculation.
Upload molecules
ACC is able to read the molecular structure and charge information from the most common file formats. Nonetheless, because it was designed to handle molecules of all kinds and size, ACC generally requires that the input files follow the formal guidelines established for each format.
In order to produce chemically relevant atomic charges using EEM, it is necessary that the structure of the molecule be complete. No crucial parts should be missing. If parts of the structure are missing, appropriate cappings should be included. All protons should be present according to the relevant protonation state. Since ACC does not currently include functionality for editing the molecular structure, you must address these issues prior to uploading the molecule into ACC. For example, you may use a server like pdb2pqr to assign protonation states, add protons and subsequently estimate the total molecular charge.
ACC does check valences, and produces a missing H warning if they are not satisfied. Despite the warning though, ACC allows to proceed with the charge calculation step, as it might not always be possible to obtain a perfect structure (e.g., when working with low resolution structures of extremely large complexes). The results from such calculations may not have chemical meaning in their absolute values, but they can be very useful when comparing sets of charges (open vs closed conformation, free vs bound state, etc.).
Input files generally contain atom type information. Many different atom type schemes are used in different modeling projects. Moreover, many times the output is not even standardized between different applications implementing the same atom type scheme. ACC attempts to be a general utility, and currently implements only the detection of chemical elements. If the atom types in the input file differ from chemical elements, ACC will report them as unknown chemical elements, and these atoms will be skipped during the EEM calculation (they will not contribute to the EEM matrix ). A similar problem will arise if the atom type information is not found at the expected place in the file. In the future, a more complex parsing algorithm may be implemented in ACC in order to cover the most common atom type schemes (e.g., AMBER, OPLS, etc.). Currently, the atom type parsing problem can be worked around either by uploading input files which adhere to the formal guidelines for their respective formats and contain atom types according to chemical elements, or by creating an EEM parameter set with special parameters for those atom types which ACC finds problematic.
If the chain ID is not explicitly included in the input file, but the molecule contains multiple chains with overlapping residue serial numbers, the results will not be meaningful for the affected residues, and possibly even in the vicinity of these residues. ACC provides check chain ID warnings both before and after the computation if this problem is detected, so that the input file can be corrected.
If bond information is not explicitly included in the input file, ACC will attempt to compute this information based on the molecular structure. This algorithm may assign wrong bond information when interatomic distances vary significantly from the expected norms. This behavior may only affect calculations using EEM parameter sets which distinguish between atom types based on bond information.
Setup computation
Once you have uploaded your molecule(s), ACC parses the molecular structure and redirects you to the ACC Setup page.
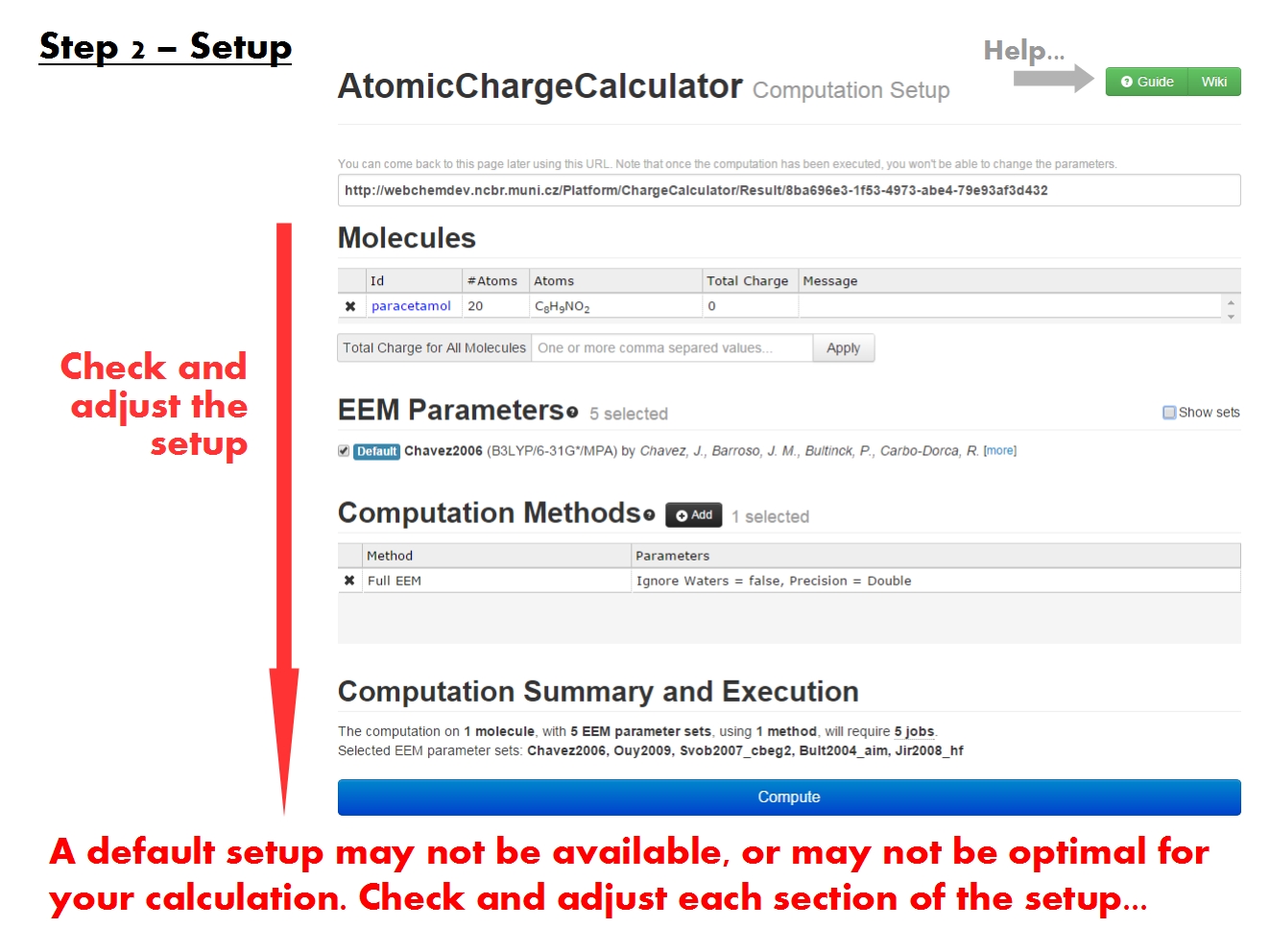
ACC generally tries to prefill the setup form with suitable options based on the molecule(s) you uploaded. It commonly happens that you can start the calculation immediately after loading the molecule. Nonetheless, the setup has a few critical points you should check manually before proceeding.
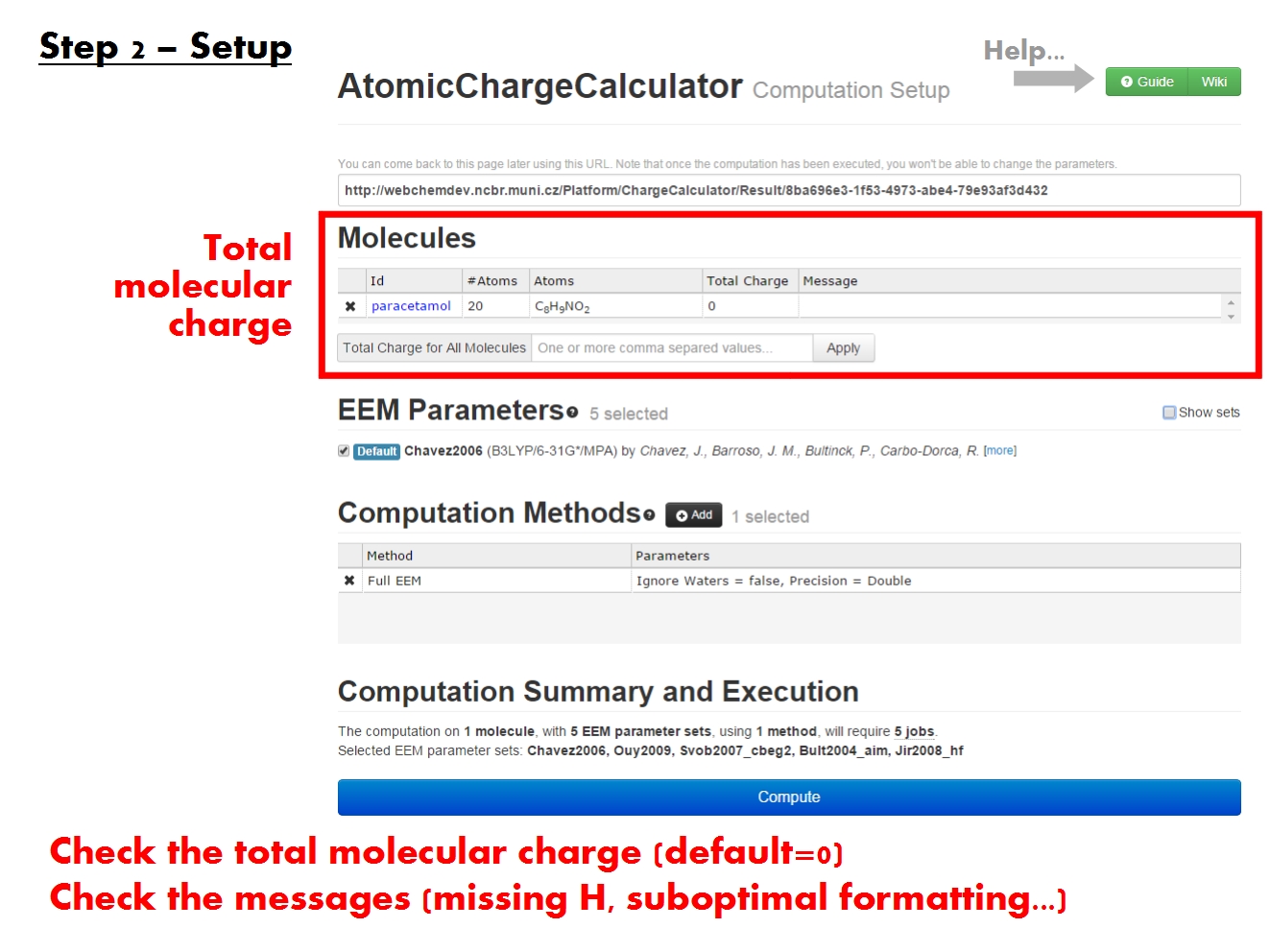
Set total charge
The total molecular charge quantifies the amount of electron density that will be distributed across the molecule during the EEM calculation. The total molecular charge plays an important role in the quality of the ACC results. By default, ACC assumes that all molecules are neutral. If this is not the case for your molecule(s), you must indicate so in the appropriate field. For each non-neutral molecule you uploaded, write the appropriate total charge value in the Total charge column. If all molecules you uploaded have the same charge, use the Total Charge for All Molecules field, and click Apply.
The total molecular charge must be in tune with the structure of the molecule. Specifically, it correlates with the number of unsatisfied valences in the molecule. For this reason, ACC checks valences, and produces a missing H warning if they are not satisfied, suggesting the molecule may not be neutral. You should always check the Message column.
Pick EEM parameters
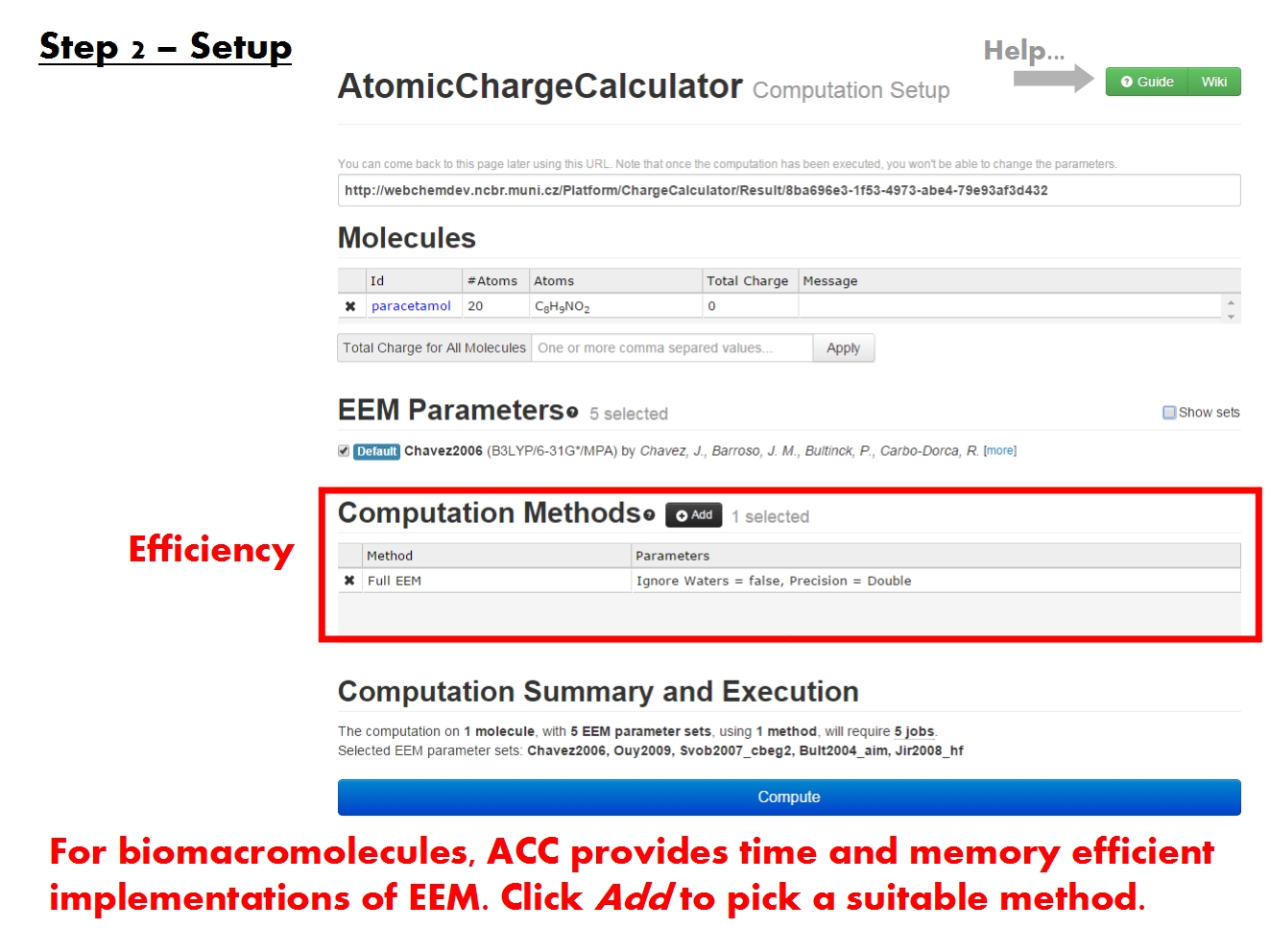
The
If the atom type information in the input file differ from chemical elements, ACC will report an unknown chemical elements warning, and these atoms will be skipped during the EEM calculation (they will not contribute to the EEM matrix ). A similar problem will arise if the atom type information is not found at the expected place in the file. In the future, a more complex parsing algorithm may be implemented in ACC in order to cover the most common atom type schemes (e.g., AMBER, OPLS, etc.). Currently, the atom type parsing problem can be worked around either by uploading input files which adhere to the formal guidelines for their respective formats and contain atom types according to chemical elements, or by creating an EEM parameter set with special parameters for those atom types which ACC finds problematic.
Pick computation method
Start computation
Return to the Table of contents.