NEEMP:Examples
This section shows several use case examples. All of them use only data from examples directory.
NB: NEEMP is case-sensitive. Please follow carefully this section for insight on the correct syntax. Additional information can be found here.
Example 1 - Training set information
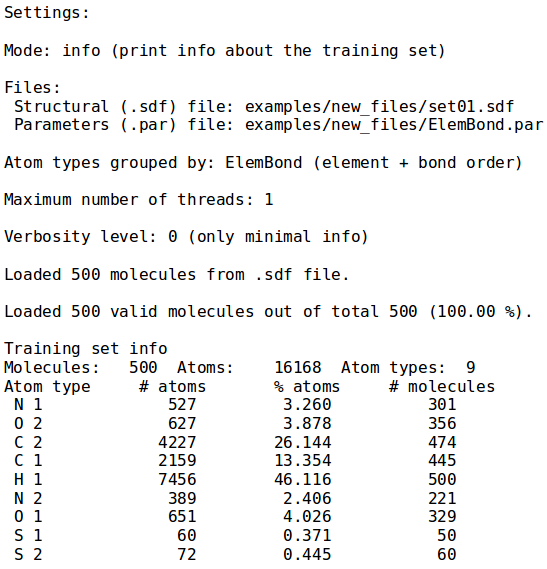
- ./neemp -m info --atom-types-by ElemBond --sdf-file examples/set01.sdf
- Prints information about training set, group atoms according to chemical element and bond order.
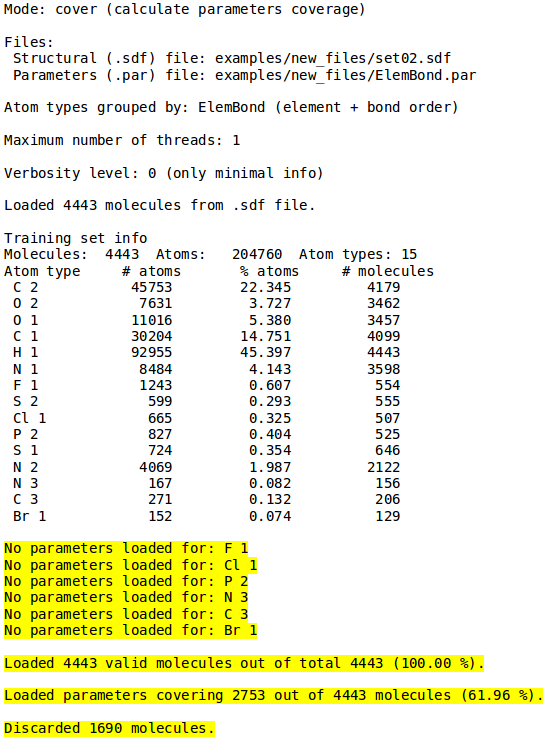
Example 2 - Coverage validation
- ./neemp -m cover -sdf-file examples/set02.sdf --par-file examples/Element.par --atom-types-by Element
- Calculate coverage of supplied EEM parameters and molecules set.
Example 3 - Calculation mode
- ./neemp -m charges --sdf-file examples/set01.sdf --par-file examples/ElemBond.par --chg-out-file eem_charges --max-threads 8
- Compute EEM charges and store them into the file eem_charges. Use up to 8 threads for computation.
For more information on this mode and its output, refer to Calculation mode section.
For details on eem_charges output file, see CHG file paragraph, as the format is the same. The only different regards the third column, since in this case the EEM charges are listed in place of the ab-initio charges.
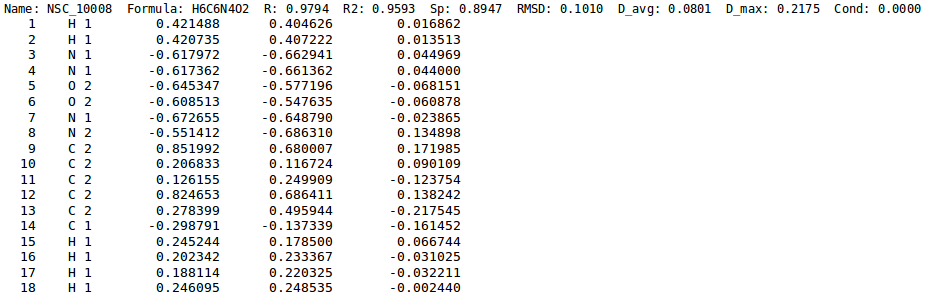
Example 4 - Quality validation
- ./neemp -m cross --sdf-file examples/set02.sdf --chg-file examples/charges.chg --par-file examples/Element.par --chg-stats-out stats --atom-types-by Element 2> warns > log
- Perform cross-validation of EEM parameters for atoms grouped by element only. Save standard output into the file log and warnings into the file warns. Moreover outputs charge statistics for each molecule into the file stats.
For more information on this mode click here.
.
Example 5 - Parametrization mode
- ./neemp -m params --sdf-file examples/set01.sdf --chg-file examples/charges.chg --par-out-file new_parameters.par --chg-stats-out-file stats
- Performs EEM parametrization, saves parameters into the file new_parameters.par, outputs charge statistics for each molecule into the file stats. No discarding is used.
NB: the parameters set file new_parameters.par presents the same identical format and layout as described here.
For additional information click here.
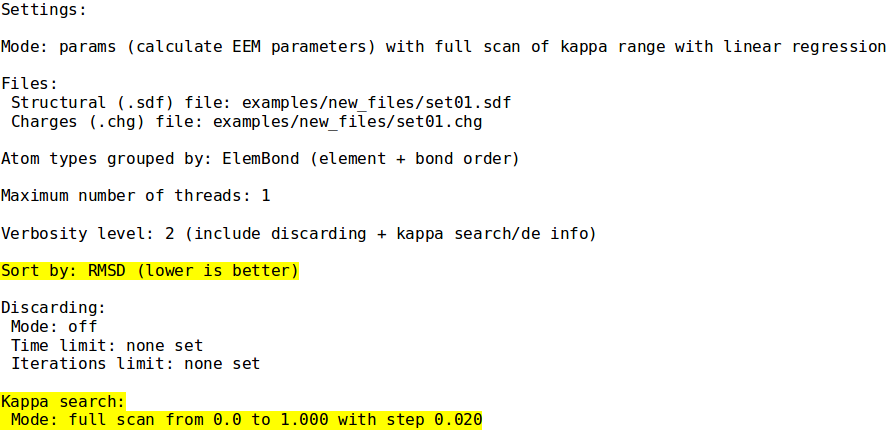
Example 6 - Parametrization mode k search
- ./neemp -m params --sdf-file examples/set01.sdf --chg-file examples/charges.chg --kappa-max 1.0 --fs-precision 0.02 --sort-by RMSD -vv
- Similar to previous example, use custom range for k. Select best parameters according to RMSD. Print k search progress.
Reference to parametrization paragraph and options list if necessary.
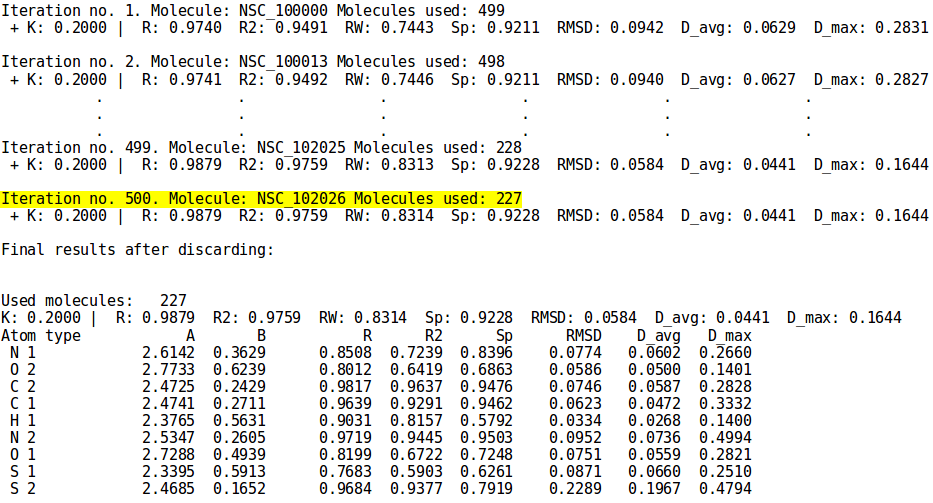
Example 7 - Parametrization mode simple discard
- ./neemp -m params --sdf-file examples/set01.sdf --chg-file examples/charges.chg --discard simple -v --check-charges --limit-iters 600 --limit-time 00:30:00
- Perform simple discarding and print its progress. Issue warning about molecules with abnormal values of statistical descriptors. The duration of the discarding procedure can be at most 600 iterations or 30 minutes (time format HH:MM:SS), whichever is reached first.
Example 8 - Parametrization mode DE-MIN
- ./neemp -m params -p de --sdf-file examples/set01.sdf --chg-file examples/charges.chg --om-pop-size 50 --random-seed 1234 -vv
- Compute parameters for the given molecules in file set01.sdf and ab-initio charges in charges.chg. The chosen optimization method: guided minimization will create 50 vectors (each vector consists of all parameters) and minimized reasonably good ones for 1000 iterations. The best of them will be minimized again, for 500 iterations. A user-defined seed is used and higher level of verbosity is used.
For additional information click here.