ChargeCalculator:Interpretation of results: Difference between revisions
| (46 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Once the calculation is complete, '''ACC''' updates the page with the unique URL which had been assigned to your computation. This page is organized into a '''Synopsis page''' covering results for all molecules, and one or more '''Specifics pages''' covering detailed results for each molecule. | |||
=Synopsis page= | =Synopsis page= | ||
''' | The '''ACC Synopsis page''' contains an overview of your computation, which might have consisted of multiple jobs for multiple molecules. You may download all the results now, or return to this page later via this URL. You may also inspect the results directly in your web browser. | ||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ACC downloadable results consist of molecular structure files containing atomic charges (.mol2 and .pqr formats), statistics of the results (atomic charges, correlations between sets of charges from different jobs), information about all jobs (setup, run time, warnings, errors). Note that if EEM parameters were missing for some atoms, the charge for these atoms will appear as 0.000 in the .mol2 and .pqr files, and as "-" in the .csv files. The .wprop files will not list these atoms at all. | ||
For each molecule, the table lists the number of atoms and chemical formula, the time it took '''ACC''' to complete all jobs pertaining to that molecule, along with the number of warnings and errors it encountered. Note that the timing listed by '''ACC''' for the first molecule in the table is actually the total computation time for all molecules, and thus it may seem disproportionately large compared to the timing listed for each of the remaining molecules in the table. | |||
In the table with molecules, click on a molecule name (Id) to visualize and analyze the results for this molecule in detail. Each [[ChargeCalculator:Terminology#Molecule | ''molecule'']] is identified according to the name of the input file, and comprises all structural elements in the input file, from simple compounds to biomacromolecular complexes made up of proteins, nucleic acids, ligands, ions, water, etc. For each molecule, your computation may have consisted of several [[ChargeCalculator:Terminology#Molecule | ''jobs'']], in which case all the results will be available for analysis. | |||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" width="650px" | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<!--Col1-->[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide | |<!--Col1-->[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 12.jpg| 650px]] | ||
|<!--Col2-->[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide | |<!--Col2-->[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 13.jpg| 650px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<!--Col1--> | |<!--Col1-->The '''ACC Synopsis page''' contains an overview of all '''ACC''' jobs for all molecules. The results are available for download, and are accessible at this URL. | ||
|<!--Col2--> | |<!--Col2-->In the table with molecules on the '''ACC Synopsis page''', click on the molecule name (Id) to visualize and analyze the results for this molecule in detail in its respective '''Specifics page'''. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 17: | Line 23: | ||
=Specifics page= | =Specifics page= | ||
The '''ACC Specifics page''' contains the results of all atomic charge calculation jobs pertaining to ''a single molecule''. The molecule is identified according to the name of the original input file. The '''Specifics page''' is organized into functional tabs which allow to view and analyze various parts of the data directly in your browser. | |||
The | ==Summary== | ||
[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 14.jpg|thumb|right|650px|The '''Summary tab''' contains basic information about the input molecule and the setup of the calculation, a list of all sets of charges produced during the computation, along with all errors and warnings associated with any of the ''jobs'' ACC ran for this molecule.]] | |||
The '''Summary tab''' contains an overview of the calculation. First, it provides basic information about the input molecule and the setup of the calculation. | |||
Remember that the ''molecule'' comprises all structural elements present in the input file, regardless of annotations. Each molecule is characterized here by its molecular formula describing the ''atomic composition'', and the ''total charge'' distributed across the constituent atoms based on EEM. The total duration of all jobs for this molecule is also given, and the individual job timing is available as a log file for download with the rest of the results. | |||
Note that multiple ''jobs'' may have been run for this molecule. A job is defined based on the molecule and its total charge, along with the EEM parameter set and computation method used. Each job produces a distinct ''set of charges'' with a unique ID encoding the EEM parameter set, method and total molecular charge. If the original input file contained values of atomic charges, these are also stored in a charge set named according to the input file, and marked by ''ref''. All charge sets are available for analysis in the other tabs of the '''Specifics page'''. | |||
Warnings and errors generated while processing the input files and running the calculation are listed in the right panel of the '''Summary tab'''. Each job will have its own list of errors and warnings. Jobs with errors generally do not produce any charge set, while jobs with warnings do. Warnings inform about some action taken under unexpected circumstances (e.g, defaulting to different parameters for certain atoms), or draw attention to aspects which may represent issues (e.g., missing H atoms). | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
The | ==Raw Data== | ||
[[File:ACC_FirstTimeUserGuide 15.jpg|thumb|right|650px| The '''Raw Data tab''' allows to view the values of atomic or residue charges, depending on the ''Atom Grouping'' menu. Each column shows charges resulted from a single job, or read from the input file. The filter works on the atom or residue labels, and can parse regular expressions.]] | |||
The ''raw data'' is available in tabular form, and refers to the actual values of atomic charges resulted from the EEM calculation, or read in from the input file. Residue charges are also available if residue annotations are available in the input file. No additional statistics are included here. Note that if EEM parameters were missing for some atoms, the charge for these atoms will appear here as "n/a". The same is true for residues made up only of such atoms, namely their total charge will be "n/a". | |||
'''ACC''' allows access to the raw data at more levels of resolution (''atom grouping''). In the ''Atom Grouping'' menu, pick ''Atoms'' to list atomic charges, or ''Residues'' to list residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue). | |||
The first column in the ''Raw data table'' is reserved for the ''labels''. The labels uniquely identify each element of the molecule, based on the resolution chosen in the ''Atom Grouping'' menu. Labels for ''Atoms'' contain the atom type, atom name, atom serial number and residue of origin. Labels for ''Residues'' contain the residue name, residue serial number, chain identifier and number of atoms in the residue. Entries can be sorted according to the atom or residue serial number. | |||
Each further column in the ''Raw data table'' contains atom or residue charges from a single ''charge set''. A charge set resulted from a single job (identified by the EEM parameter set, method and total molecular charge), or was read from the input file (identified by the file name and marked by ''ref''). | |||
Use the filter in the upper right corner of the page to display only the table entries of interest. The filter is applied on the ''label'', works as you type, and updates the appearance of the table. The most effective approach is to use regular expressions (try your hand [https://regex101.com/ here] for more complex queries). Note the counter next to the filter, which gives the number of records displayed in the table. | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
==Analyze== | ==Analyze== | ||
[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide | [[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 16.jpg|thumb|right|650px| The '''Analyze tab''' provides statistics about atomic or residue charges. The contents of the graph are dictated by the panel on the left.]] | ||
'''ACC''' provides several statistical descriptors for the results at more levels of resolution, in graphical and tabular form. The menus on the left dictate contents of the graph to the right, and of the ''Raw Data'' table below. | |||
The graph displays the ''value'' of a statistical descriptor for charges on ''groups of atoms'', according to a certain ''property''. For example, the ''minimum charge'' of ''atoms'' according to their ''chemical element''. Each column in the graph represents the results from a single set of charges, either produced by a single job (defined by EEM parameter set, computation method, and total molecular charge), or read from the input file (identified by the file name and marked by ''ref''). | |||
The menu ''Atom Grouping'' gives the level of resolution. Pick ''Atoms'' to display statistics on atomic charges, or ''Residues'' to display statistics on residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue). Residue-based statistics are available only if residue annotations are present in the input file. | |||
The menu ''Group Property'' sets the specific property based on which the statistics are calculated for a certain ''atom grouping''. For example, statistics on all ''atoms with a certain chemical element'', or statistics on all ''polar residues''. | |||
''Plot Value'' refers to the specific statistical descriptor displayed in the graph. For example, the ''standard deviation'' of the charge on atoms with a certain chemical element. | |||
The ''Raw Data'' table provides a tabular representation of all statistical descriptors for each set of charges, and its contents depend on the ''Atom Grouping'' and ''Group Property'' menus above. | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
==Compare== | ==Compare== | ||
[[File: | [[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 17.jpg|thumb|right|650px| The '''Compare tab''' allows to compare atomic or residue charges resulted from different jobs, or read from the input file. The contents of the graph are dictated by the panel on the left.]] | ||
'''ACC''' allows to compare sets of charges at more levels of resolution, in graphical and tabular form. These sets of charges may have resulted from different jobs, or were read from the input file. | |||
The graph provides a statistical comparison between two sets of charges, each displayed on one axis (X vs Y), at atomic or residue resolution. For example, you may compare between formal residue charges given in the input file, and residue charges as computed by EEM. The menus on the left dictate the contents of the graph, and of the ''Raw Data'' table below. | |||
The resolution of the graph depends on the ''Atom Grouping'' menu. Pick ''Atoms'' to compare atomic charges, or ''Residues'' to compare residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue). Remember that residue-based statistics are available only if residue annotations are present in the input file. | |||
Use the menus for the ''X axis'' and ''Y axis'' to pick the sets of charges to compare. Each set of charges was produced by a single job (identified by EEM parameter set, computation method and total molecular charge), or was read from the input file (identified by the input file name and marked by ''ref''). If you find the default XY ranges unsuitable for comparing the charge sets you chose, you may adjust them manually. | |||
The number of data points depends on ''Atom Grouping''. Comparison statistics are computed using the entire datasets, but only 2500 data points display by default. '''ACC''' generally doesn't cause problems even when displaying 10000 data points, but it depends on the amount of memory available for your browser. If in trouble, just reload the page. Note that since outliers are displayed first, the graph might suggest the two charge sets are more dissimilar than the comparison statistics say. Therefore, always check the graph title and the ''Raw Data'' table on the left. | |||
The ''Raw Data'' table provides a tabular representation of the statistical comparison between a specific set of charges and all other charge sets available for this molecule. The contents depend on the ''Atom Grouping'' menu above. | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
==3D Model== | ==3D Model== | ||
[[File: | [[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 18.jpg|thumb|right|650px| The '''3D Model tab''' displays a 3D model of your molecule, based either on atomic or residue resolution. The contents of the visualization window are dictated by the panel on the left.]] | ||
'''ACC''' allows a few basic charge visualization options to aid in interpreting the results of the atomic charge calculation. You may need to update your browser and driver version to be able to run the 3D visualizer (see the [[ChargeCalculator:Technical_details#Requirements | requirements]]). The panels on the left dictate the contents of the visualization window on the right, which allows you to display and manipulate with a ''3D model of your molecule colored according to charges''. The legend for mouse controls for manipulating with the 3D model (rotation, zoom) is available in the right bottom corner of the visualization window. | |||
Note that 3D visualization is generally memory consuming, so you should consider the settings before attempting to visualize the 3D model of your molecule. '''ACC''' allows you to customize the 3D model of the molecule in several ways. If you would like to revert to the default visualization settings suggested by '''ACC''', click ''Set default parameters''. If you feel confident that your visualization settings are suitable, click ''Update'' to display the 3D model of your molecule colored according to charges. You may need to use the ''Update'' button several times as you adjust the visualization state, as some changes will not take effect otherwise. | |||
With respect to building and coloring the 3D model, the menu ''Atom Grouping'' gives the level of resolution. Pick ''Atoms'' to build the 3D model based on ''atomic positions'' and color it by ''atomic charges''. Pick ''Residues'' to build the 3D model based on ''residue positions'' (coordinates averaged over all atoms in each residue) and color it by ''residue charges'' (sum of atomic charges for each residue). Note that residue positions and charges are available only if residue annotations are present in the input file. In the absence of such information, '''ACC''' will display the 3D model as a simple sphere colored according to the total molecular charge, and placed at the center of the molecule (coordinates averaged over all atoms in the molecule). | |||
Several sets of charges might be available for the given molecule. Each set of charges was produced by a single job (identified by EEM parameter set, computation method and total molecular charge), or was read from the input file (identified by the input file name and marked by ''ref''). By default, '''ACC''' will color the 3D molecule using the first set in its list. To change this, simply pick another set from the ''Display Charges'' menu. Further, instead of coloring by charges, it is sometimes useful to color by differences between two sets of charges. For example, to see how the presence of water changes the charge profile of the molecular surface. To do this, tick ''Show Differences'' and pick the second set of charges from the menu. Note that the differences displayed are always calculated as ''Display Charges'' - ''Show Differences''. | |||
'''ACC''' enables several basic modes for displaying the 3D model of your molecule, depending on the ''Atom Grouping''. Each display mode has additional options you may wish to tweak. For example, display the protein using ''Cartoons'', and the ligands using ''Balls and Sticks'', but hide water molecules. In all cases, make sure to adjust the ''display detail'' according to your needs. Specifically, for large biomolecular complexes, start with ''lower levels of display detail'', and work your way up if you feel unsatisfied with the quality of the display. To reduce the complexity you may also find it useful to build the 3D model using the ''Residues atom grouping''. If in trouble, just reload the page. | |||
If you find the default coloring scheme unsuitable, you may manually adjust the colors using the palette. Similarly, you may find it useful to manually adjust the scale by setting ''Min./Max. Value'', and skew the color scale by ''Mid. Value''. Further adjustment to the coloring scheme is accessible by the parameter ''Value Gap'', and allows to emphasize the visual difference in charge distribution in different areas of the molecule. Emphasis increases with ''Value Gap''. | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
[[File:ACC FirstTimeUserGuide 19.jpg|thumb|right|650px| To find out what the display and analysis options mean, take advantage of all the help available as interactive guides and tool tips. ]] | |||
Finally, if you don't know what something means or how it works, don't forget that there is plenty of help available directly on the '''ACC''' web pages. Hover the mouse over any keyword you do not understand to reveal a useful tool tip. Click on any of the buttons marking the interactive guides. Note that such guides are available for the entire '''Results page''', and for any of the tabs on the '''Specifics page'''. | |||
'''The complete list of keywords involved in the interpretation of ACC results is available in the [[ChargeCalculator:Index | Index]].''' | |||
'''Return to the [[ChargeCalculator:UserManual | Table of contents]].''' | '''Return to the [[ChargeCalculator:UserManual | Table of contents]].''' | ||
Latest revision as of 17:12, 29 May 2015
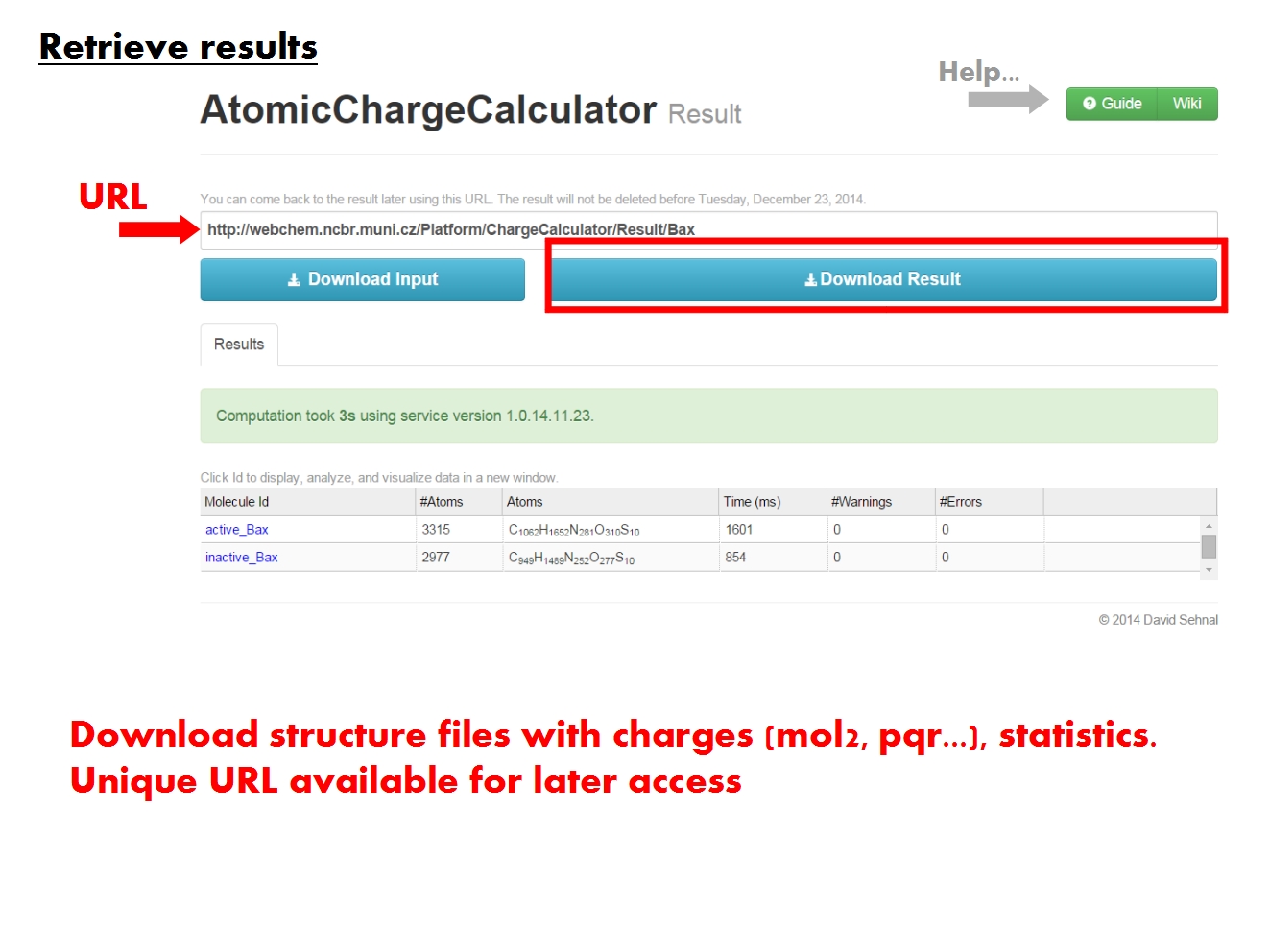
Once the calculation is complete, ACC updates the page with the unique URL which had been assigned to your computation. This page is organized into a Synopsis page covering results for all molecules, and one or more Specifics pages covering detailed results for each molecule.
Synopsis page
[edit]The ACC Synopsis page contains an overview of your computation, which might have consisted of multiple jobs for multiple molecules. You may download all the results now, or return to this page later via this URL. You may also inspect the results directly in your web browser.
ACC downloadable results consist of molecular structure files containing atomic charges (.mol2 and .pqr formats), statistics of the results (atomic charges, correlations between sets of charges from different jobs), information about all jobs (setup, run time, warnings, errors). Note that if EEM parameters were missing for some atoms, the charge for these atoms will appear as 0.000 in the .mol2 and .pqr files, and as "-" in the .csv files. The .wprop files will not list these atoms at all.
For each molecule, the table lists the number of atoms and chemical formula, the time it took ACC to complete all jobs pertaining to that molecule, along with the number of warnings and errors it encountered. Note that the timing listed by ACC for the first molecule in the table is actually the total computation time for all molecules, and thus it may seem disproportionately large compared to the timing listed for each of the remaining molecules in the table.
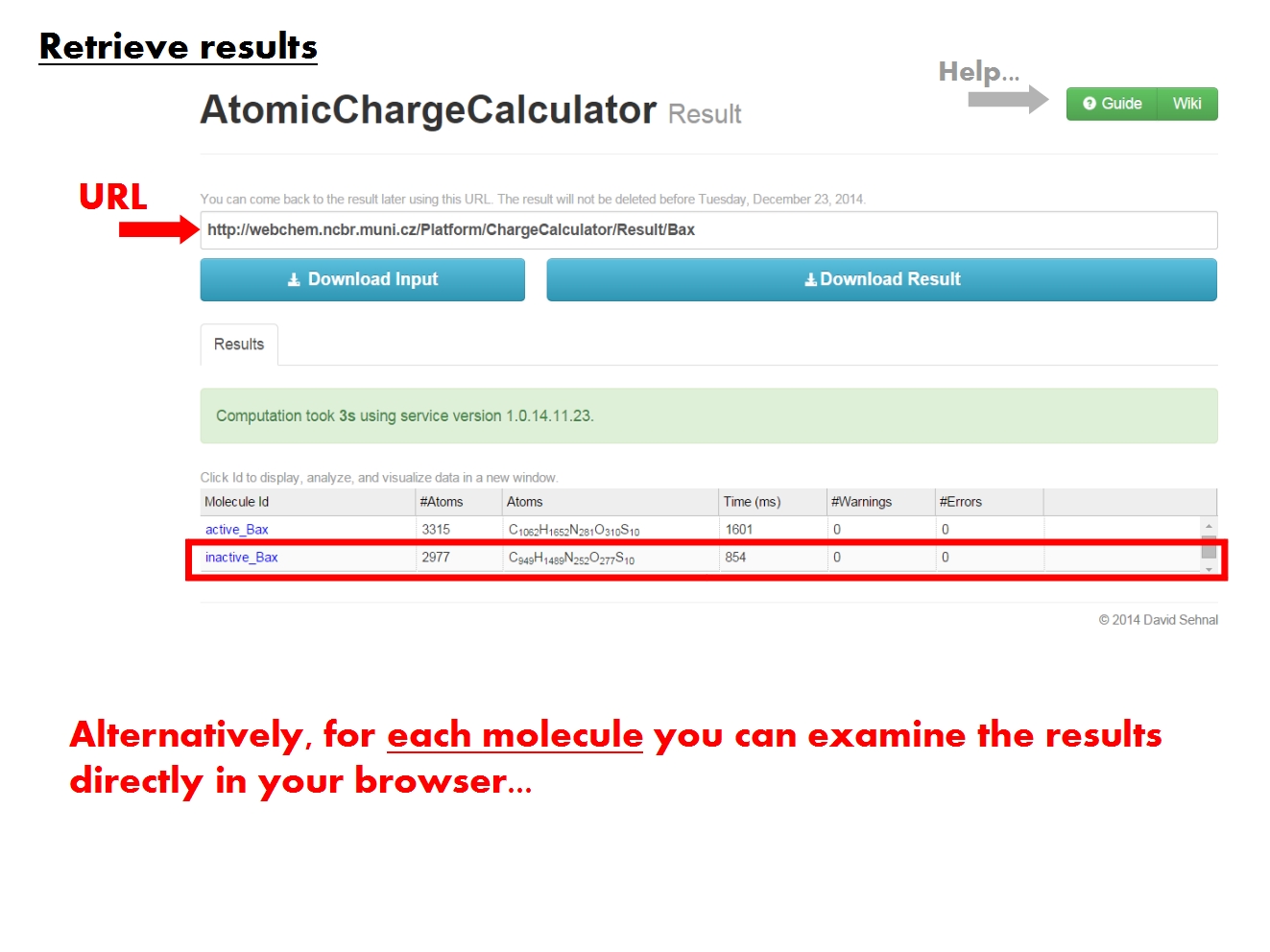
In the table with molecules, click on a molecule name (Id) to visualize and analyze the results for this molecule in detail. Each molecule is identified according to the name of the input file, and comprises all structural elements in the input file, from simple compounds to biomacromolecular complexes made up of proteins, nucleic acids, ligands, ions, water, etc. For each molecule, your computation may have consisted of several jobs, in which case all the results will be available for analysis.
Specifics page
[edit]The ACC Specifics page contains the results of all atomic charge calculation jobs pertaining to a single molecule. The molecule is identified according to the name of the original input file. The Specifics page is organized into functional tabs which allow to view and analyze various parts of the data directly in your browser.
Summary
[edit]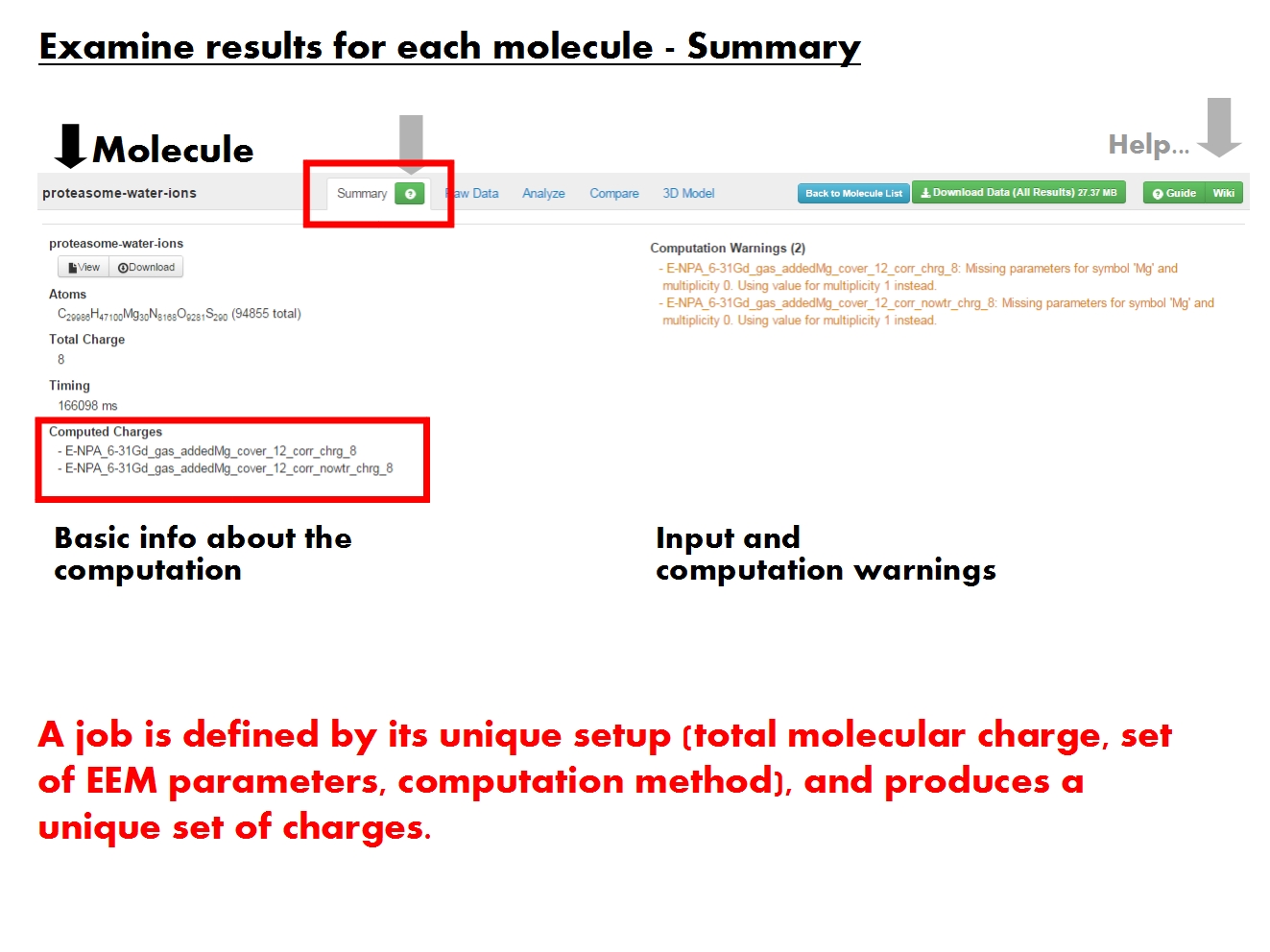
The Summary tab contains an overview of the calculation. First, it provides basic information about the input molecule and the setup of the calculation. Remember that the molecule comprises all structural elements present in the input file, regardless of annotations. Each molecule is characterized here by its molecular formula describing the atomic composition, and the total charge distributed across the constituent atoms based on EEM. The total duration of all jobs for this molecule is also given, and the individual job timing is available as a log file for download with the rest of the results.
Note that multiple jobs may have been run for this molecule. A job is defined based on the molecule and its total charge, along with the EEM parameter set and computation method used. Each job produces a distinct set of charges with a unique ID encoding the EEM parameter set, method and total molecular charge. If the original input file contained values of atomic charges, these are also stored in a charge set named according to the input file, and marked by ref. All charge sets are available for analysis in the other tabs of the Specifics page.
Warnings and errors generated while processing the input files and running the calculation are listed in the right panel of the Summary tab. Each job will have its own list of errors and warnings. Jobs with errors generally do not produce any charge set, while jobs with warnings do. Warnings inform about some action taken under unexpected circumstances (e.g, defaulting to different parameters for certain atoms), or draw attention to aspects which may represent issues (e.g., missing H atoms).
Raw Data
[edit]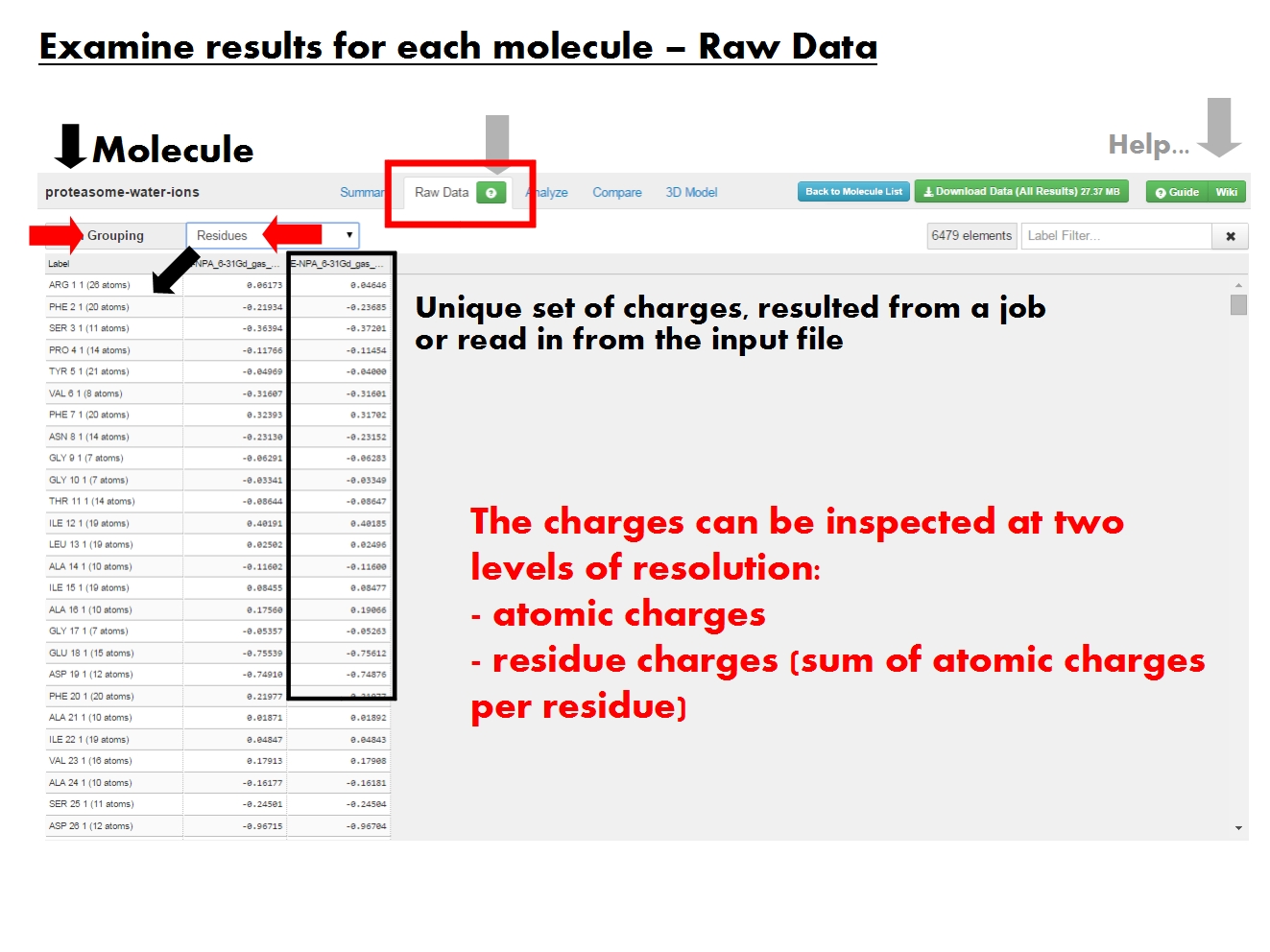
The raw data is available in tabular form, and refers to the actual values of atomic charges resulted from the EEM calculation, or read in from the input file. Residue charges are also available if residue annotations are available in the input file. No additional statistics are included here. Note that if EEM parameters were missing for some atoms, the charge for these atoms will appear here as "n/a". The same is true for residues made up only of such atoms, namely their total charge will be "n/a".
ACC allows access to the raw data at more levels of resolution (atom grouping). In the Atom Grouping menu, pick Atoms to list atomic charges, or Residues to list residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue).
The first column in the Raw data table is reserved for the labels. The labels uniquely identify each element of the molecule, based on the resolution chosen in the Atom Grouping menu. Labels for Atoms contain the atom type, atom name, atom serial number and residue of origin. Labels for Residues contain the residue name, residue serial number, chain identifier and number of atoms in the residue. Entries can be sorted according to the atom or residue serial number.
Each further column in the Raw data table contains atom or residue charges from a single charge set. A charge set resulted from a single job (identified by the EEM parameter set, method and total molecular charge), or was read from the input file (identified by the file name and marked by ref).
Use the filter in the upper right corner of the page to display only the table entries of interest. The filter is applied on the label, works as you type, and updates the appearance of the table. The most effective approach is to use regular expressions (try your hand here for more complex queries). Note the counter next to the filter, which gives the number of records displayed in the table.
Analyze
[edit]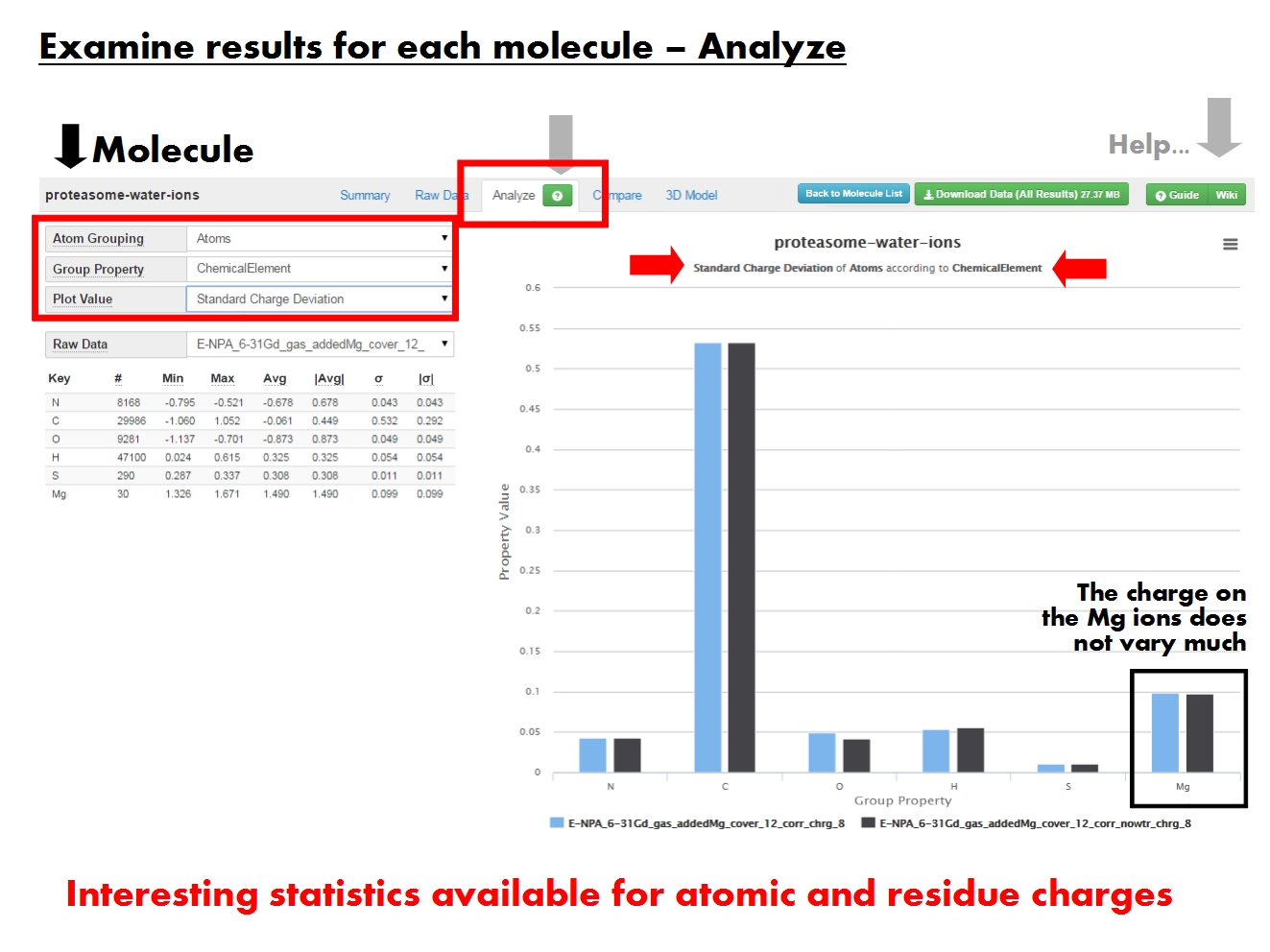
ACC provides several statistical descriptors for the results at more levels of resolution, in graphical and tabular form. The menus on the left dictate contents of the graph to the right, and of the Raw Data table below.
The graph displays the value of a statistical descriptor for charges on groups of atoms, according to a certain property. For example, the minimum charge of atoms according to their chemical element. Each column in the graph represents the results from a single set of charges, either produced by a single job (defined by EEM parameter set, computation method, and total molecular charge), or read from the input file (identified by the file name and marked by ref).
The menu Atom Grouping gives the level of resolution. Pick Atoms to display statistics on atomic charges, or Residues to display statistics on residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue). Residue-based statistics are available only if residue annotations are present in the input file.
The menu Group Property sets the specific property based on which the statistics are calculated for a certain atom grouping. For example, statistics on all atoms with a certain chemical element, or statistics on all polar residues.
Plot Value refers to the specific statistical descriptor displayed in the graph. For example, the standard deviation of the charge on atoms with a certain chemical element.
The Raw Data table provides a tabular representation of all statistical descriptors for each set of charges, and its contents depend on the Atom Grouping and Group Property menus above.
Compare
[edit]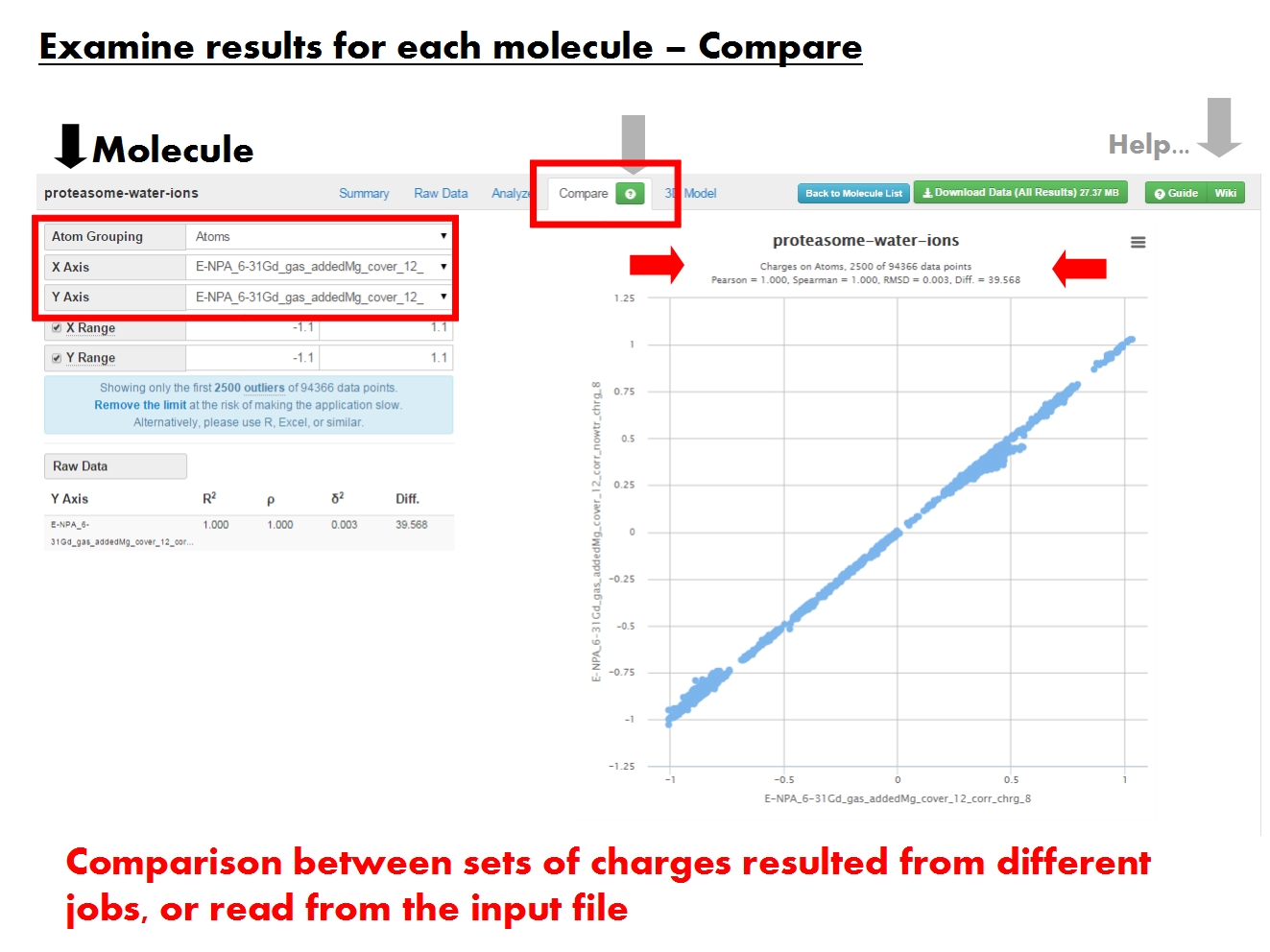
ACC allows to compare sets of charges at more levels of resolution, in graphical and tabular form. These sets of charges may have resulted from different jobs, or were read from the input file.
The graph provides a statistical comparison between two sets of charges, each displayed on one axis (X vs Y), at atomic or residue resolution. For example, you may compare between formal residue charges given in the input file, and residue charges as computed by EEM. The menus on the left dictate the contents of the graph, and of the Raw Data table below.
The resolution of the graph depends on the Atom Grouping menu. Pick Atoms to compare atomic charges, or Residues to compare residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue). Remember that residue-based statistics are available only if residue annotations are present in the input file.
Use the menus for the X axis and Y axis to pick the sets of charges to compare. Each set of charges was produced by a single job (identified by EEM parameter set, computation method and total molecular charge), or was read from the input file (identified by the input file name and marked by ref). If you find the default XY ranges unsuitable for comparing the charge sets you chose, you may adjust them manually.
The number of data points depends on Atom Grouping. Comparison statistics are computed using the entire datasets, but only 2500 data points display by default. ACC generally doesn't cause problems even when displaying 10000 data points, but it depends on the amount of memory available for your browser. If in trouble, just reload the page. Note that since outliers are displayed first, the graph might suggest the two charge sets are more dissimilar than the comparison statistics say. Therefore, always check the graph title and the Raw Data table on the left.
The Raw Data table provides a tabular representation of the statistical comparison between a specific set of charges and all other charge sets available for this molecule. The contents depend on the Atom Grouping menu above.
3D Model
[edit]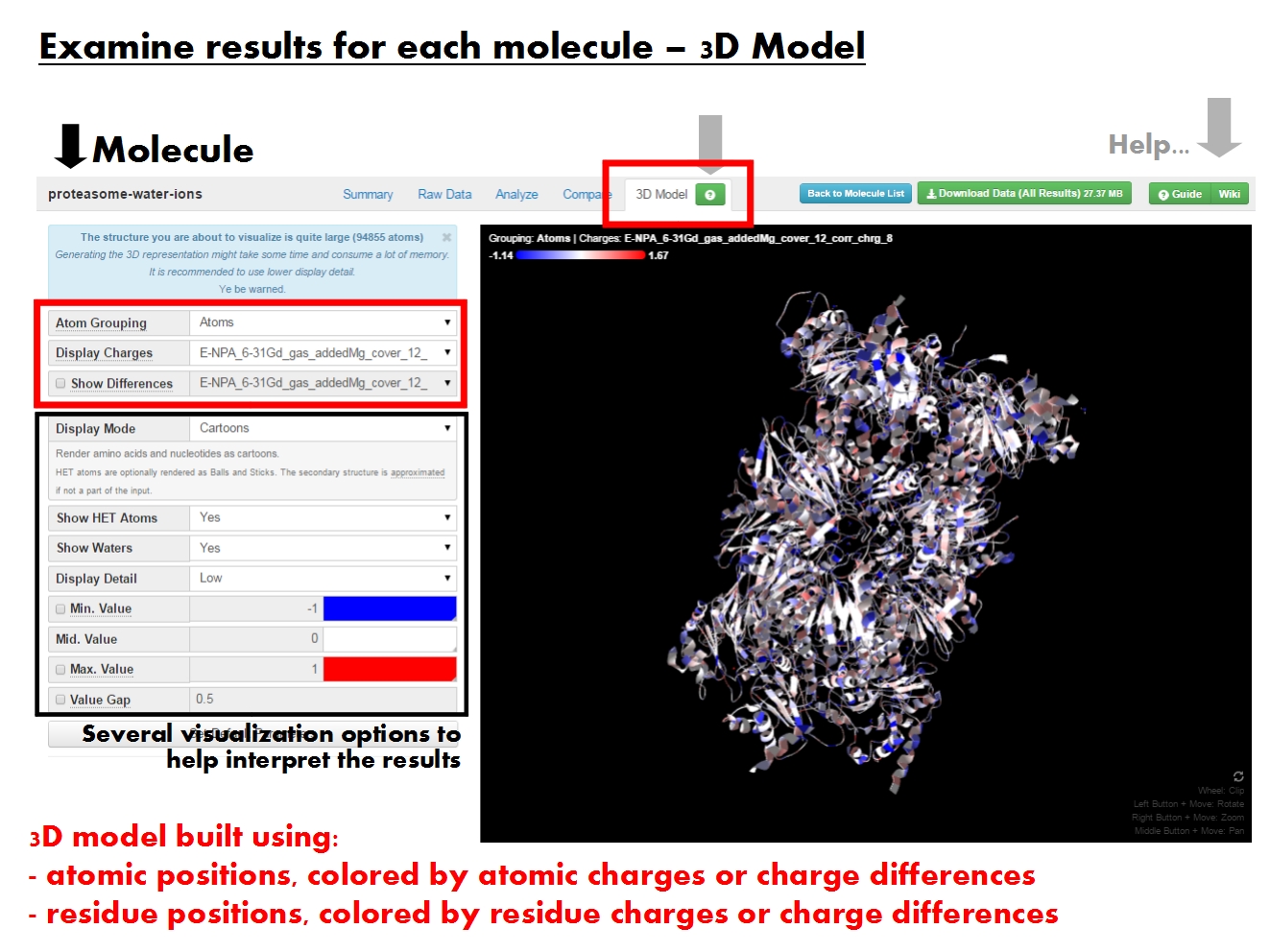
ACC allows a few basic charge visualization options to aid in interpreting the results of the atomic charge calculation. You may need to update your browser and driver version to be able to run the 3D visualizer (see the requirements). The panels on the left dictate the contents of the visualization window on the right, which allows you to display and manipulate with a 3D model of your molecule colored according to charges. The legend for mouse controls for manipulating with the 3D model (rotation, zoom) is available in the right bottom corner of the visualization window.
Note that 3D visualization is generally memory consuming, so you should consider the settings before attempting to visualize the 3D model of your molecule. ACC allows you to customize the 3D model of the molecule in several ways. If you would like to revert to the default visualization settings suggested by ACC, click Set default parameters. If you feel confident that your visualization settings are suitable, click Update to display the 3D model of your molecule colored according to charges. You may need to use the Update button several times as you adjust the visualization state, as some changes will not take effect otherwise.
With respect to building and coloring the 3D model, the menu Atom Grouping gives the level of resolution. Pick Atoms to build the 3D model based on atomic positions and color it by atomic charges. Pick Residues to build the 3D model based on residue positions (coordinates averaged over all atoms in each residue) and color it by residue charges (sum of atomic charges for each residue). Note that residue positions and charges are available only if residue annotations are present in the input file. In the absence of such information, ACC will display the 3D model as a simple sphere colored according to the total molecular charge, and placed at the center of the molecule (coordinates averaged over all atoms in the molecule).
Several sets of charges might be available for the given molecule. Each set of charges was produced by a single job (identified by EEM parameter set, computation method and total molecular charge), or was read from the input file (identified by the input file name and marked by ref). By default, ACC will color the 3D molecule using the first set in its list. To change this, simply pick another set from the Display Charges menu. Further, instead of coloring by charges, it is sometimes useful to color by differences between two sets of charges. For example, to see how the presence of water changes the charge profile of the molecular surface. To do this, tick Show Differences and pick the second set of charges from the menu. Note that the differences displayed are always calculated as Display Charges - Show Differences.
ACC enables several basic modes for displaying the 3D model of your molecule, depending on the Atom Grouping. Each display mode has additional options you may wish to tweak. For example, display the protein using Cartoons, and the ligands using Balls and Sticks, but hide water molecules. In all cases, make sure to adjust the display detail according to your needs. Specifically, for large biomolecular complexes, start with lower levels of display detail, and work your way up if you feel unsatisfied with the quality of the display. To reduce the complexity you may also find it useful to build the 3D model using the Residues atom grouping. If in trouble, just reload the page.
If you find the default coloring scheme unsuitable, you may manually adjust the colors using the palette. Similarly, you may find it useful to manually adjust the scale by setting Min./Max. Value, and skew the color scale by Mid. Value. Further adjustment to the coloring scheme is accessible by the parameter Value Gap, and allows to emphasize the visual difference in charge distribution in different areas of the molecule. Emphasis increases with Value Gap.
Finally, if you don't know what something means or how it works, don't forget that there is plenty of help available directly on the ACC web pages. Hover the mouse over any keyword you do not understand to reveal a useful tool tip. Click on any of the buttons marking the interactive guides. Note that such guides are available for the entire Results page, and for any of the tabs on the Specifics page.
The complete list of keywords involved in the interpretation of ACC results is available in the Index.
Return to the Table of contents.